선릉역 1번 출구
TCP 네트워킹 - 2 본문
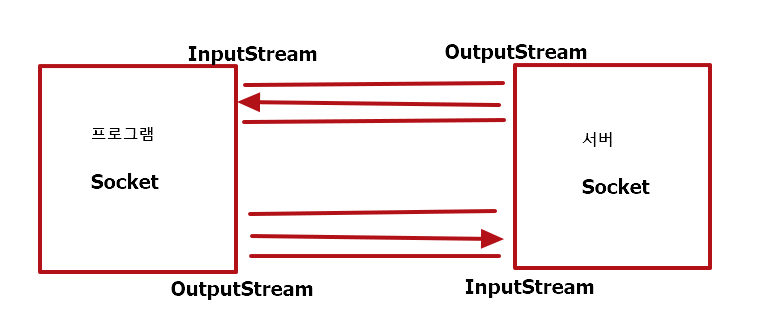
클라이언트가 연결을 요청(connect)하고, 서버가 수락(accept)하면 양쪽의 Socket 객체로부터 각각 입력 스트림(InputStream)과 출력 스트림(OutputStream)을 얻을 수 있음
데이터 송신: 데이터를 byte[] 배열로 생성하고, 이것을 매개값으로 OutputStream의 wirte() 메소드 호출
데이터 수신: 데이터를 저장할 byte[] 배열 생성 후, 이것을 매개값으로 InputStream의 read() 메소드 호출
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket();
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5001));
while(true) {
System.out.println("[연결 기다림]");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InetSocketAddress isa = (InetSocketAddress) socket.getRemoteSocketAddress();
System.out.println("[연결 수락함]" + isa.getHostName());
byte[] bytes = null;
String message = null;
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
bytes = new byte[100];
int readByteCount = is.read(bytes);
message = new String(bytes, 0, readByteCount, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("[데이터 받기 성공]: " + message);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
message = "hello client";
bytes = message.getBytes("UTF-8");
os.write(bytes);
os.flush();
System.out.println("[데이터 보내기 성공]");
os.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
}
} catch(Exception e) {}
if(!serverSocket.isClosed()) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch(IOException e1) {}
}
}
}Server
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Socket socket = null;
try {
socket = new Socket();
System.out.println("[연결 요청]");
socket.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 5001));
System.out.println("[연결 성공]");
byte[] bytes = null;
String message = null;
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
message = "hello server";
bytes = message.getBytes("UTF-8");
os.write(bytes);
os.flush();
System.out.println("[데이터 보내기 성공]");
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
bytes = new byte[100];
int readByteCount = is.read(bytes);
message = new String(bytes, 0, readByteCount, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("[데이터 받기 성공]: " + message);
os.close();
is.close();
} catch(Exception e) {}
if(!socket.isClosed()) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch(IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}client
데이터를 받기 위해 InputStream의 read() 메소드를 호출하면 상대방이 데이터를 보내기 전까지는 블로킹(blocking)됨
read() 메소드가 블로킹 해제되고 리턴되는 경우는?
| 블로킹이 해제되는 경우 | 리턴값 |
| 상대방이 데이터를 보냄 | 읽은 바이트 수 |
| 상대방이 정상적으로 Socket의 close()를 호출 | -1 |
| 상대방이 비정상적으로 종료 | IOException |
블로킹 Blocking
- A 함수가 B 함수를 호출 할 때, B 함수가 자신의 작업이 종료되기 전까지 A 함수에게 제어권을 돌려주지 않는 것
논블로킹 Non-blocking
- A 함수가 B 함수를 호출 할 때, B 함수가 제어권을 바로 A 함수에게 넘겨주면서, A 함수가 다른 일을 할 수 있도록 하는 것
참고 사이트
'Computer > Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| network 수업 정리(1) - start (0) | 2023.01.30 |
|---|---|
| chatgpt를 활용한 tcp의 3way handshake 질의 응답(1) (0) | 2023.01.29 |
| TCP 네트워킹 - 1 (0) | 2023.01.02 |
| [Packet Tracer] 무선랜 암호(WPA2-PSK, WPA2-Enterprise) (2) | 2022.12.22 |
| [Packet Tracer] 무선랜 (0) | 2022.12.21 |
Comments

